ICT
Intent
Career Opportunities in ICT
The study of ICT & Computing allows you to develop skills that are well-suited to many different career choices. Some examples of careers you could pursue include website designer, systems analyst, game designer, network manager, software developer, systems engineer, ICT support, games developer, app developer, teacher, media assistant, cybersecurity specialist, artificial intelligence developer, and mobile technology developer. ICT & Computing fosters logical thinking skills, making it an excellent fit for any job involving problem-solving. Additionally, most office-based employment relies on ICT & Computing, and having a qualification in this field will open many doors for you.
ICT & Computing is recognized and valued by all employers and universities. The wide range of skills and knowledge fostered by the subject allows students to develop as individuals. Most universities offer courses in ICT & Computing, providing students with the opportunity for further development.
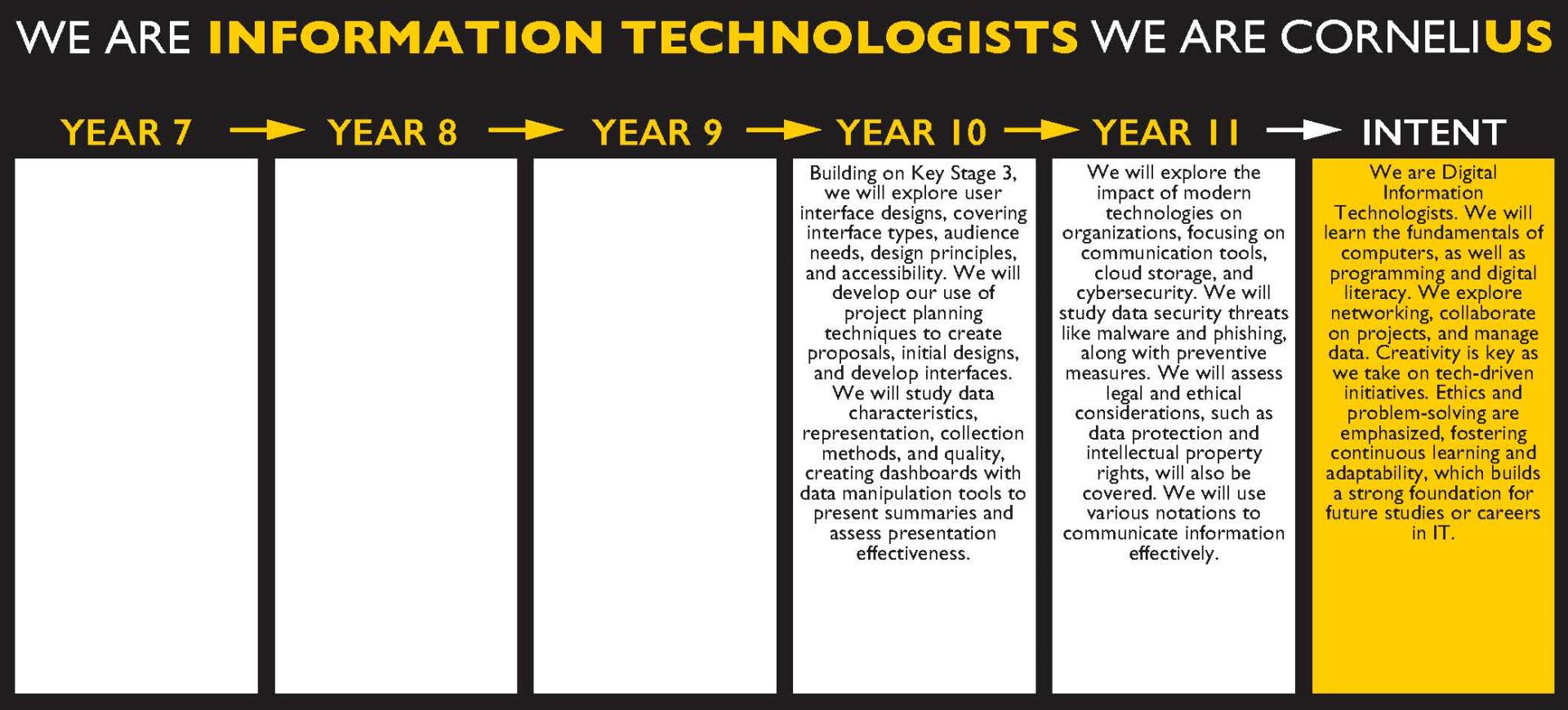
Year 10 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Exploring User Interface Design Principles and Project Planning techniques"
|
Component 1: Learning Aim A: What is a user interface? Introduction to user interfaces – basic and moving on to complex user interfaces Audience needs Design principles Designing an efficient user interface Component 1: Learning Aim B: Project planning Creating a project plan Creating an initial design Component 1: Learning Aim C Develop and review a user interface Refining the user interface Review their own work | Students will develop their understanding of what makes an effective user interface and how to effectively manage a project. They will use this understanding to plan, design and create a user interface. Students will develop their knowledge and understanding of different project planning techniques that can be used to plan, develop and monitor projects. Learners will develop their knowledge and understanding of different user interface design principles. Learners will then be able to select appropriate project planning techniques to be able to plan and create an effective user interface that meets a set of defined user requirements. | Through verbal Q and A in class. Practise of assignment based tasks. As the completed piece of coursework for component 1 – issued by exam board in September. |
|
Spring |
Component 2: Collecting, Presenting and Interpreting Data.
|
Learning Aim A: Investigate the role and impact of using data on individuals and organisations Characteristics of data and information Representing information Ensuring data is suitable for processing Data collection Quality of information and its impact on decision-making Sectors that use data modelling Threats to individuals Learning Aim B: Create a dashboard using data manipulation tools Data processing methods Produce a dashboard Learning Aim C: Draw conclusions and review data presentation methods Drawing conclusions based on the data How presentation affects understanding | Students will understand the characteristics of data and information and how they help organisations in decision making. They will use data manipulation methods to create a dashboard to present and draw conclusions from information. Students will develop their knowledge and understanding of the role and impact of using data on individuals and organisations. Students will develop their understanding on using data to ensure that effective and accurate decisions are made. Students should be able to apply appropriate data manipulation tools to manipulate data and provide clear summaries in the form of a dashboard. They will develop their knowledge and understanding of how the presentation of their dashboard can affect the effectiveness of conclusions made. | Students will understand the characteristics of data and information and how they help organisations in decision making. They will use data manipulation methods to create a dashboard to present and draw conclusions from information. Students will develop their knowledge and understanding of the role and impact of using data on individuals and organisations. Students will develop their understanding on using data to ensure that effective and accurate decisions are made. Students should be able to apply appropriate data manipulation tools to manipulate data and provide clear summaries in the form of a dashboard. They will develop their knowledge and understanding of how the presentation of their dashboard can affect the effectiveness of conclusions made |
|
Summer |
Modern technologies
|
Modern technologies - Modern teams and how the Internet has supported Global teams – how they can be based world-wide, multi-cultural, inclusive and allowed 24/7 businesses to be developed. How modern teams can be managed – using collaboration tools, communication tools, scheduling and planning tools. Focus on how stakeholders can be communicated with and how that can be effective. | Students show excellence when they can confidently explain how modern technology helps people work together across the world. They understand that global teams—made up of people from different cultures and countries—can now work together at any time, thanks to the internet. They can describe how successful teams use digital tools to plan, share ideas, and stay organized. These tools might include things like video calls, shared calendars, and task management apps. Excellent students also understand the importance of clear and respectful communication, especially when working with different people and time zones. They know how to keep everyone in the loop—including team members and other important people involved (stakeholders)—so that projects run smoothly and everyone feels included. | Q and A in class, linking topics to scenario-based questions. End of topic assessment Completing online quizzes as part of homework timetable. |
Year 11 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
The wider implications of digital systems
|
Environmental issues linked to business and personal use of computer systems, knowing the responsible disposal of old devices and systems – recycling centres, upgrading parts, safe disposal. Equal access - digital divide – between those that have/know the technology and those that don’t, what the impact is and how it can split society. Use policies within business structures – acceptable use, code of conduct etc. Data protection laws – the six elements of data handling and how business need to ensure they follow – implications if they do not. GDPR and data handling. | I will be able to communicate what the various environmental issues are and explaining how the systems can be disposed / upgraded safely. I will be able to explain what equal access to digital systems is, and the groups that could feel marginalised by technology. I will be able to communicate what the data protection act covers, and how businesses can follow it – with implications if they do not. I will identify how GDPR has come in to play and what implications this has for Europe and data handling. | Through verbal Q and A in class, worksheets working as a group or individual. As part of end of unit assessment that is exam based questions. |
|
Autumn |
Planning and communication in digital systems
|
Data Flow diagrams – Information flow diagrams (IFD) and Data Flow Diagrams (level 0 and level 1) – the various symbols that create each diagram, and how we link them together with the rules for the diagram. Flow charts – basic structure and reasoning for flow charts, understating the need for a decision making process in them and how this forms looping mechanisms. | Students will be able identify the differences between an IFD and a DFD, with clear knowledge of the components to each diagram. Students will be confident to create each chart for given scenario and apply logic for the construction of them. Students will be able construct a flow chart and demonstrate understanding of decision making and implications for outcomes. | Through verbal Q and A in class, worksheets working as a group or individual. As part of end of unit assessment that is exam based questions. |
|
Spring |
Revision for core Or Targeted revision for DIT.
|
Pathway 1 - Students who have secured targeted outcomes in January series and course as a whole, will undertake independent revision until the summer exam series. Pathway 2 - Students who did not secure expected outcomes, will continue with targeted revision for a resit in the May series. | Examination in January and/or May series. |